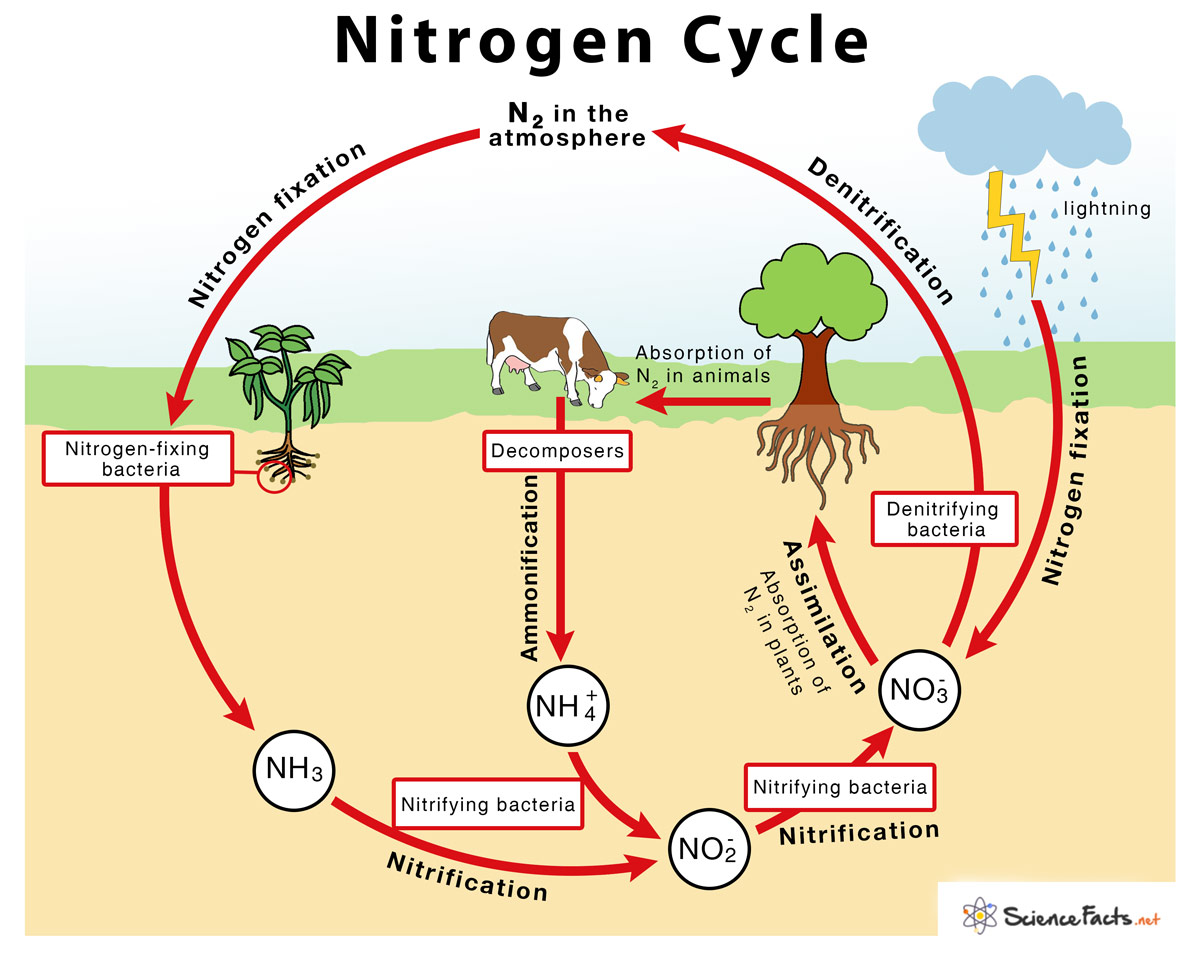
Draw Nitrogen Cycle
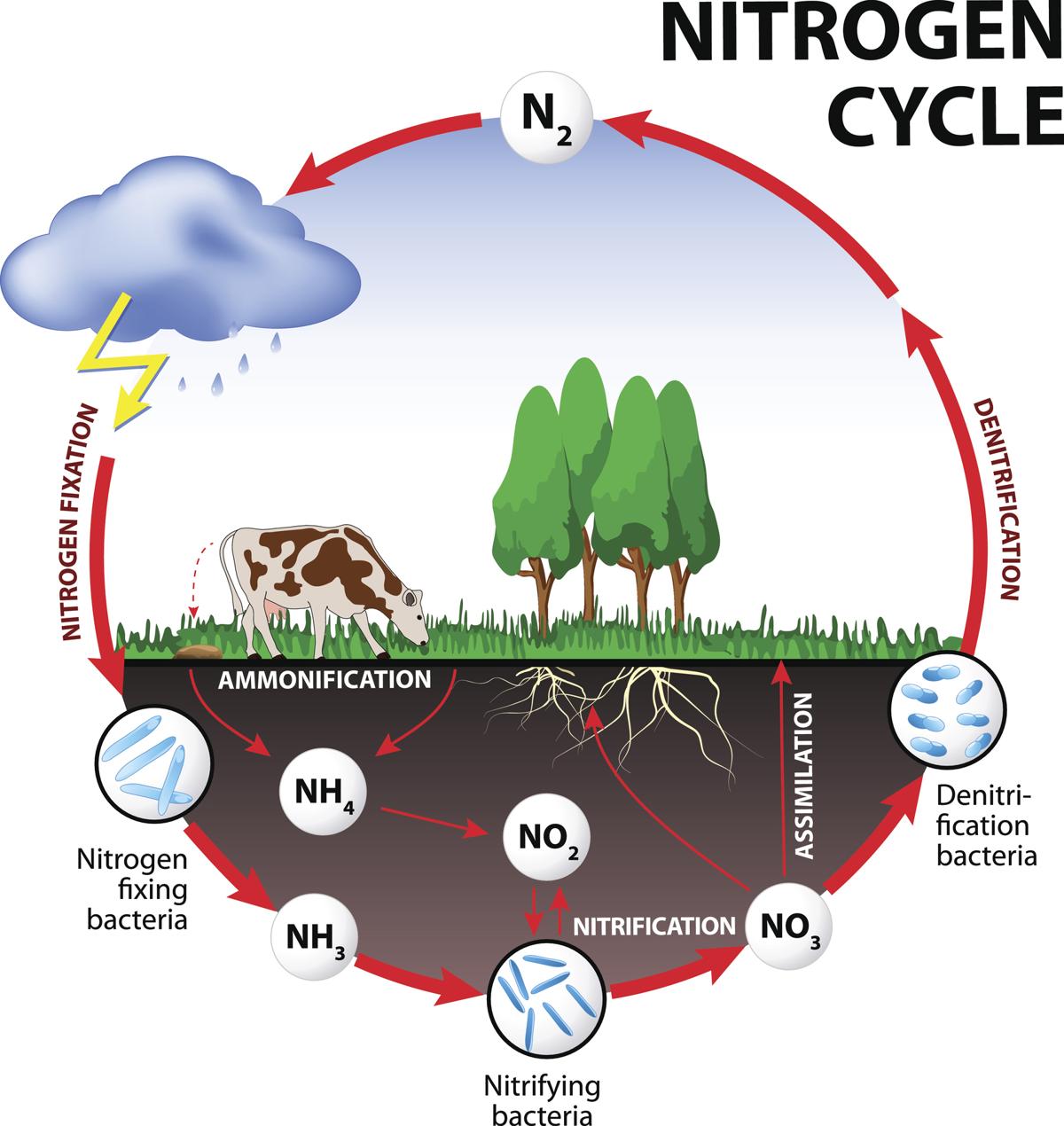
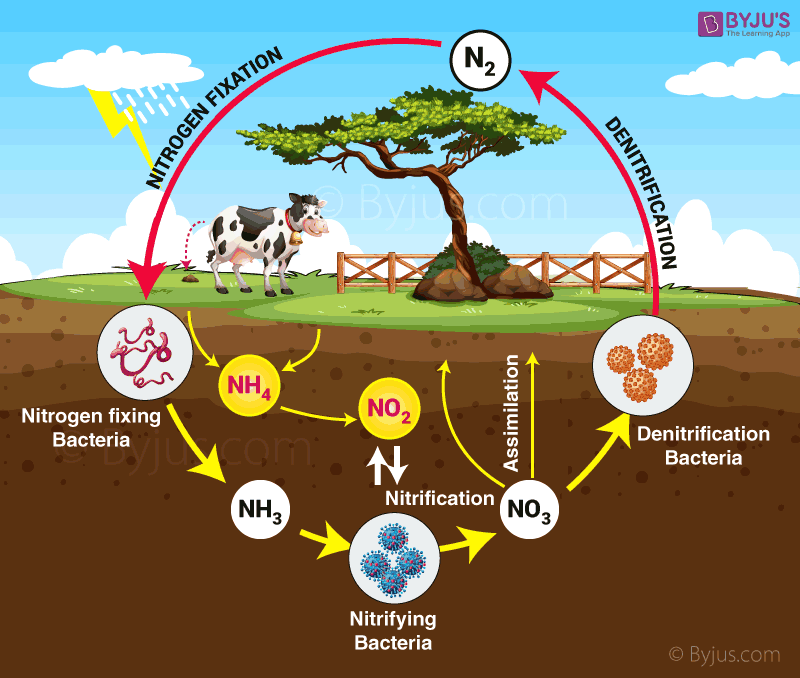
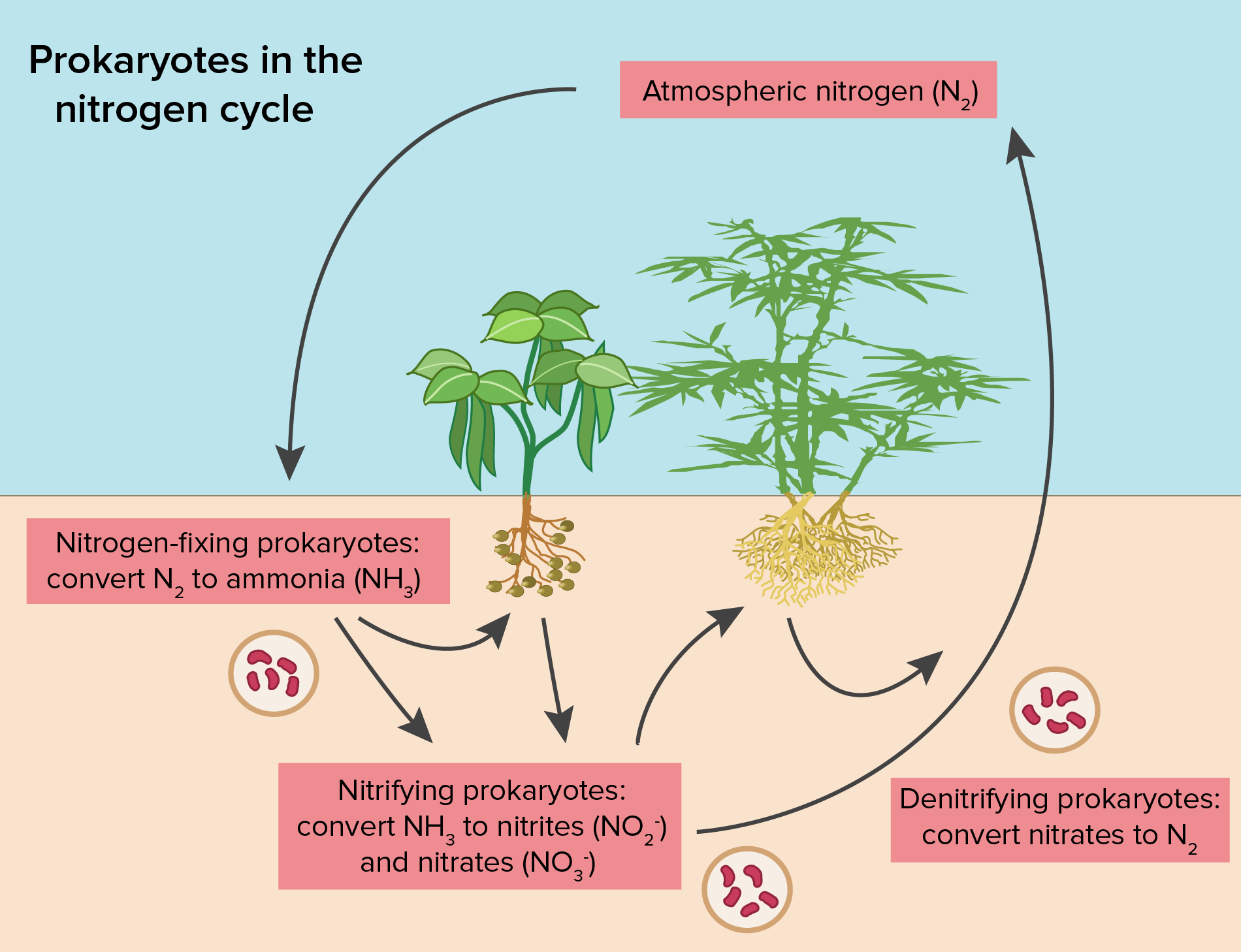
Draw Nitrogen Cycle - The conversion of nitrogen can be carried out through both biological and physical processes. Web description of the nitrogen cycle & how does it work, also learn the steps along with its importance & human impacts explained using examples & simple picture. Through the cycle, atmospheric nitrogen is converted to a form which plants can. The steps of the nitrogen cycle are described below. Nitrogen fixation occurs in three steps: Web the nitrogen cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which nitrogen is converted into multiple chemical forms as it circulates among atmospheric, terrestrial, and marine ecosystems. Web the process of converting n 2 into biologically available nitrogen is called nitrogen fixation. Nitrogen, a component of proteins and nucleic acids, is essential to life on earth. The nitrogen cycle is the cyclic movement of nitrogen in different chemical forms between living organisms and the environment. Although 78 percent by volume of the atmosphere is nitrogen gas, this abundant reservoir exists in a form unusable by most organisms. The nitrogen cycle is vital for life on earth. Human activity can release nitrogen into the environment by the combustion of fossil fuels and by the use of artificial fertilizers in agriculture. Bacteria, such as cyanobacteria, convert nitrogen into nitrogen gas via nitrogen fixation. N 2 gas is a very stable compound due to the strength of the triple bond between the nitrogen. Nitrogen is essential for life, forming a key component in amino acids, atp, and dna. Nitrogen fixation occurs in three steps: This process, known as nitrogen fixation, is primarily carried out by bacteria. Nitrogen, a component of proteins and nucleic acids, is essential to life on earth. Web the process of converting n 2 into biologically available nitrogen is called nitrogen fixation. The conversion of nitrogen can be carried out through both biological and physical processes. Web nitrogen cycle is a biogeochemical process through which nitrogen is converted into many forms, consecutively passing from the atmosphere to the soil to organism and back into the atmosphere. Web to get the forms of nitrogen they need, these organisms rely on the nitrogen cycle. This process, known as nitrogen fixation, is primarily carried out by bacteria. Human activity. Nitrogen is essential for life, forming a key component in amino acids, atp, and dna. Web to get the forms of nitrogen they need, these organisms rely on the nitrogen cycle. The nitrogen cycle is vital for life on earth. Web nitrogen cycle is a biogeochemical process through which nitrogen is converted into many forms, consecutively passing from the atmosphere. Nitrogen is essential for life, forming a key component in amino acids, atp, and dna. This process, known as nitrogen fixation, is primarily carried out by bacteria. Web nitrogen cycle, circulation of nitrogen in various forms through nature. Nitrogen, a component of proteins and nucleic acids, is essential to life on earth. Web in general, the nitrogen cycle has five. Through the cycle, atmospheric nitrogen is converted to a form which plants can. Web the nitrogen cycle is a crucial process that converts atmospheric nitrogen into a form that plants and other organisms can use. Web the process of converting n 2 into biologically available nitrogen is called nitrogen fixation. Web nitrogen cycle is a biogeochemical process through which nitrogen. The nitrogen cycle is vital for life on earth. Nitrogen fixation occurs in three steps: Web nitrogen cycle, circulation of nitrogen in various forms through nature. Through the cycle, atmospheric nitrogen is converted to a form which plants can. Nitrogen is essential for life, forming a key component in amino acids, atp, and dna. Web description of the nitrogen cycle & how does it work, also learn the steps along with its importance & human impacts explained using examples & simple picture. Although 78 percent by volume of the atmosphere is nitrogen gas, this abundant reservoir exists in a form unusable by most organisms. This process, known as nitrogen fixation, is primarily carried out. The nitrogen cycle is the cyclic movement of nitrogen in different chemical forms between living organisms and the environment. The steps of the nitrogen cycle are described below. Web nitrogen cycle, circulation of nitrogen in various forms through nature. Web description of the nitrogen cycle & how does it work, also learn the steps along with its importance & human. Nitrogen fixation occurs in three steps: Web in general, the nitrogen cycle has five steps: Although 78 percent by volume of the atmosphere is nitrogen gas, this abundant reservoir exists in a form unusable by most organisms. Nitrogen, a component of proteins and nucleic acids, is essential to life on earth. Bacteria, such as cyanobacteria, convert nitrogen into nitrogen gas. The nitrogen cycle is the cyclic movement of nitrogen in different chemical forms between living organisms and the environment. Web to get the forms of nitrogen they need, these organisms rely on the nitrogen cycle. Web in general, the nitrogen cycle has five steps: Web the process of converting n 2 into biologically available nitrogen is called nitrogen fixation. Through. Web the process of converting n 2 into biologically available nitrogen is called nitrogen fixation. Bacteria, such as cyanobacteria, convert nitrogen into nitrogen gas via nitrogen fixation. The nitrogen cycle is vital for life on earth. This process, known as nitrogen fixation, is primarily carried out by bacteria. Web to get the forms of nitrogen they need, these organisms rely. The nitrogen cycle is the cyclic movement of nitrogen in different chemical forms between living organisms and the environment. The nitrogen cycle is vital for life on earth. Web the nitrogen cycle is a crucial process that converts atmospheric nitrogen into a form that plants and other organisms can use. This process, known as nitrogen fixation, is primarily carried out by bacteria. Web description of the nitrogen cycle & how does it work, also learn the steps along with its importance & human impacts explained using examples & simple picture. Nitrogen, a component of proteins and nucleic acids, is essential to life on earth. Web the nitrogen cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which nitrogen is converted into multiple chemical forms as it circulates among atmospheric, terrestrial, and marine ecosystems. Nitrogen fixation occurs in three steps: Human activity can release nitrogen into the environment by the combustion of fossil fuels and by the use of artificial fertilizers in agriculture. It involves several processes such as nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, decay and putrefaction. N 2 gas is a very stable compound due to the strength of the triple bond between the nitrogen. Web the process of converting n 2 into biologically available nitrogen is called nitrogen fixation. Bacteria, such as cyanobacteria, convert nitrogen into nitrogen gas via nitrogen fixation. Nitrogen is essential for life, forming a key component in amino acids, atp, and dna. Through the cycle, atmospheric nitrogen is converted to a form which plants can. Web in general, the nitrogen cycle has five steps:Nitrogen Cycle Facts for Kids (Explained!) Education site
Nitrogen cycle Steps of Nitrogen cycle Online Biology Notes
How the Nitrogen Cycle Works Britannica
Nitrogen Cycle Explained Definition, Stages and Importance
Nitrogen Cycle Diagram with Steps Explained Teachoo Concepts
Explain Different Steps of Nitrogen Cycle
Understanding the Nitrogen Cycle Beginners Education AlgaeBarn
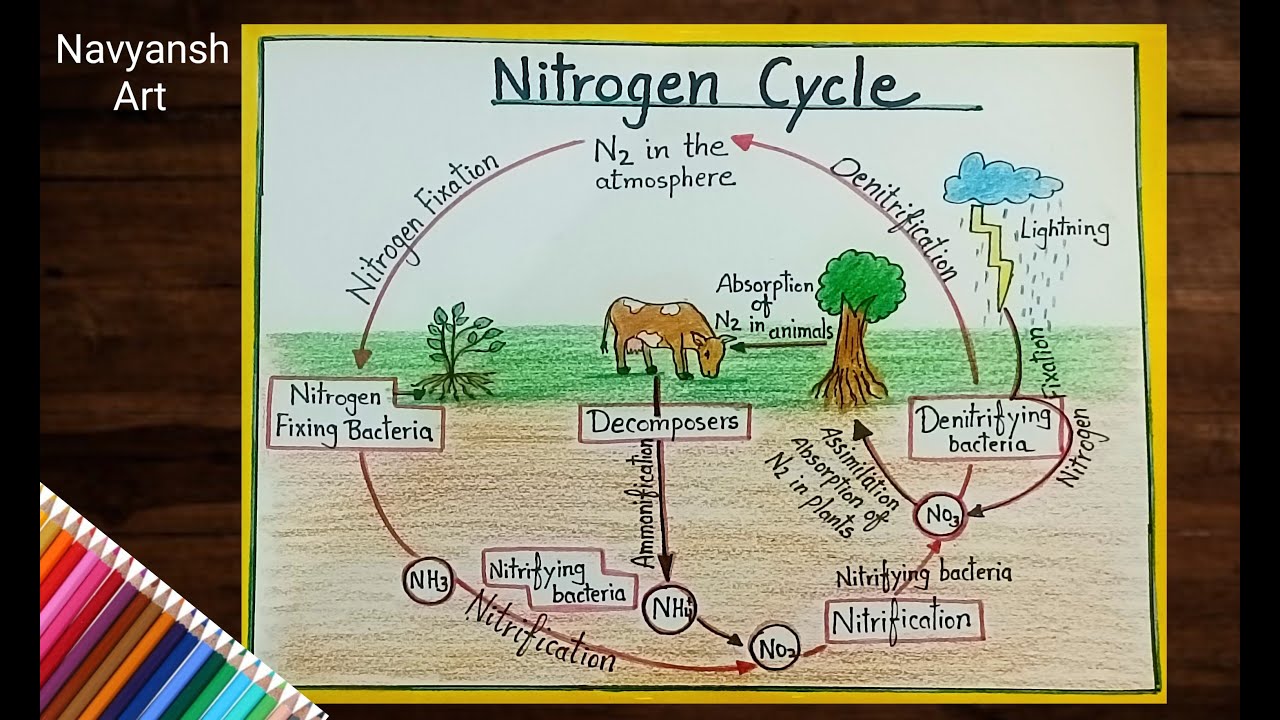
Nitrogen cycle diagram drawing/how to draw Nitrogen cycle labeled
Why is the Nitrogen Cycle So Important?
Nitrogen Cycle Definition, Steps, Importance with Diagram
Web Nitrogen Cycle, Circulation Of Nitrogen In Various Forms Through Nature.
The Steps Of The Nitrogen Cycle Are Described Below.
The Conversion Of Nitrogen Can Be Carried Out Through Both Biological And Physical Processes.
Web Nitrogen Cycle Is A Biogeochemical Process Through Which Nitrogen Is Converted Into Many Forms, Consecutively Passing From The Atmosphere To The Soil To Organism And Back Into The Atmosphere.
Related Post: